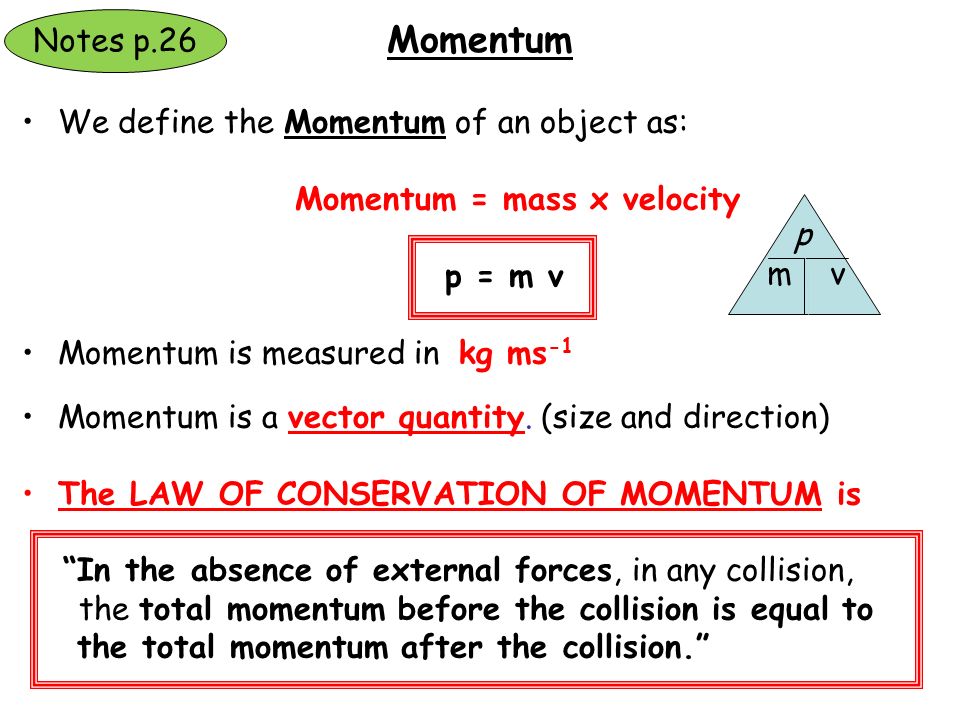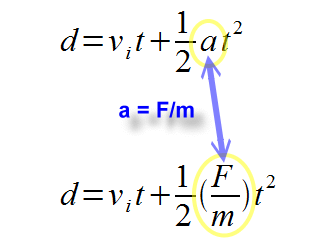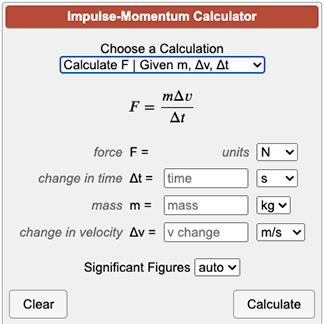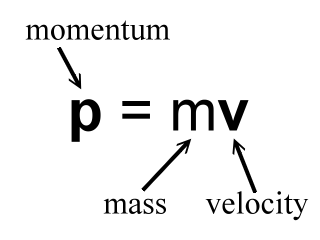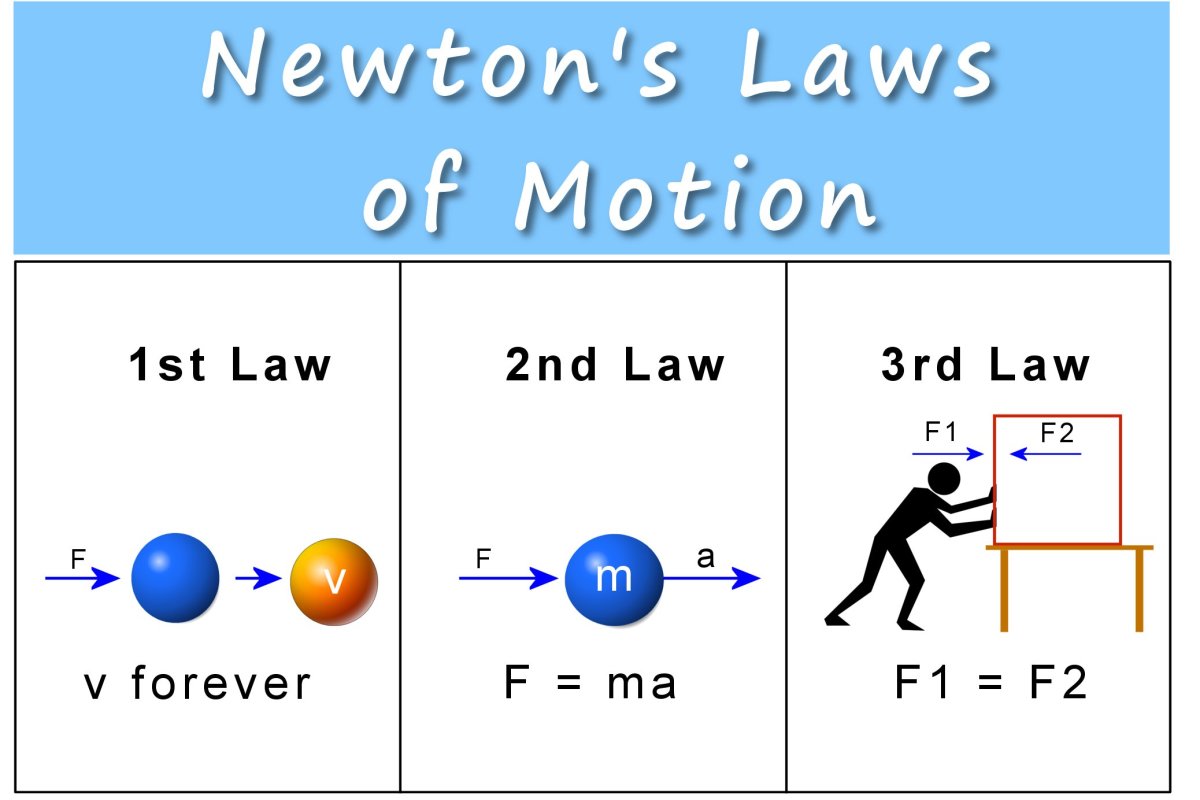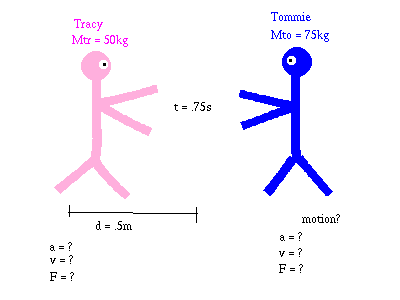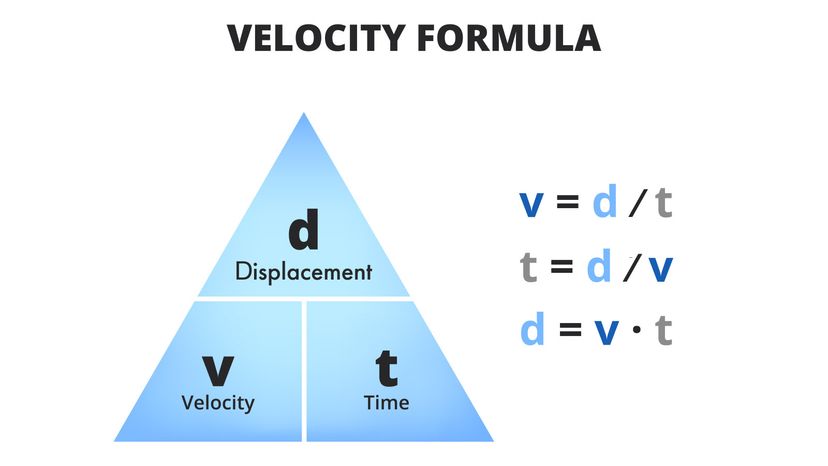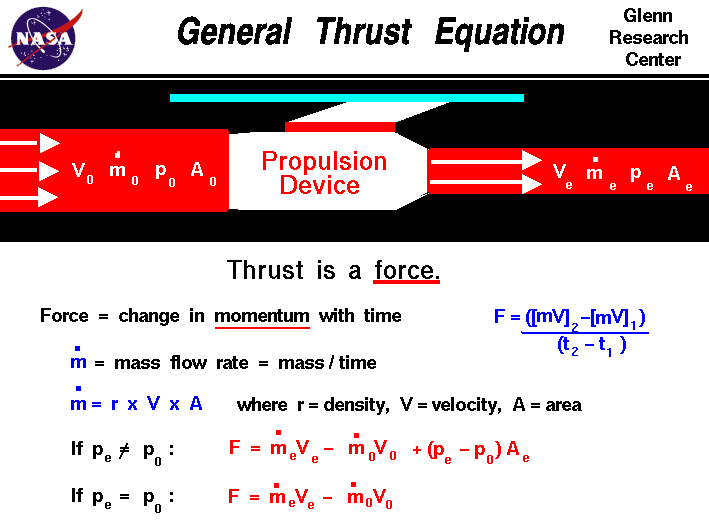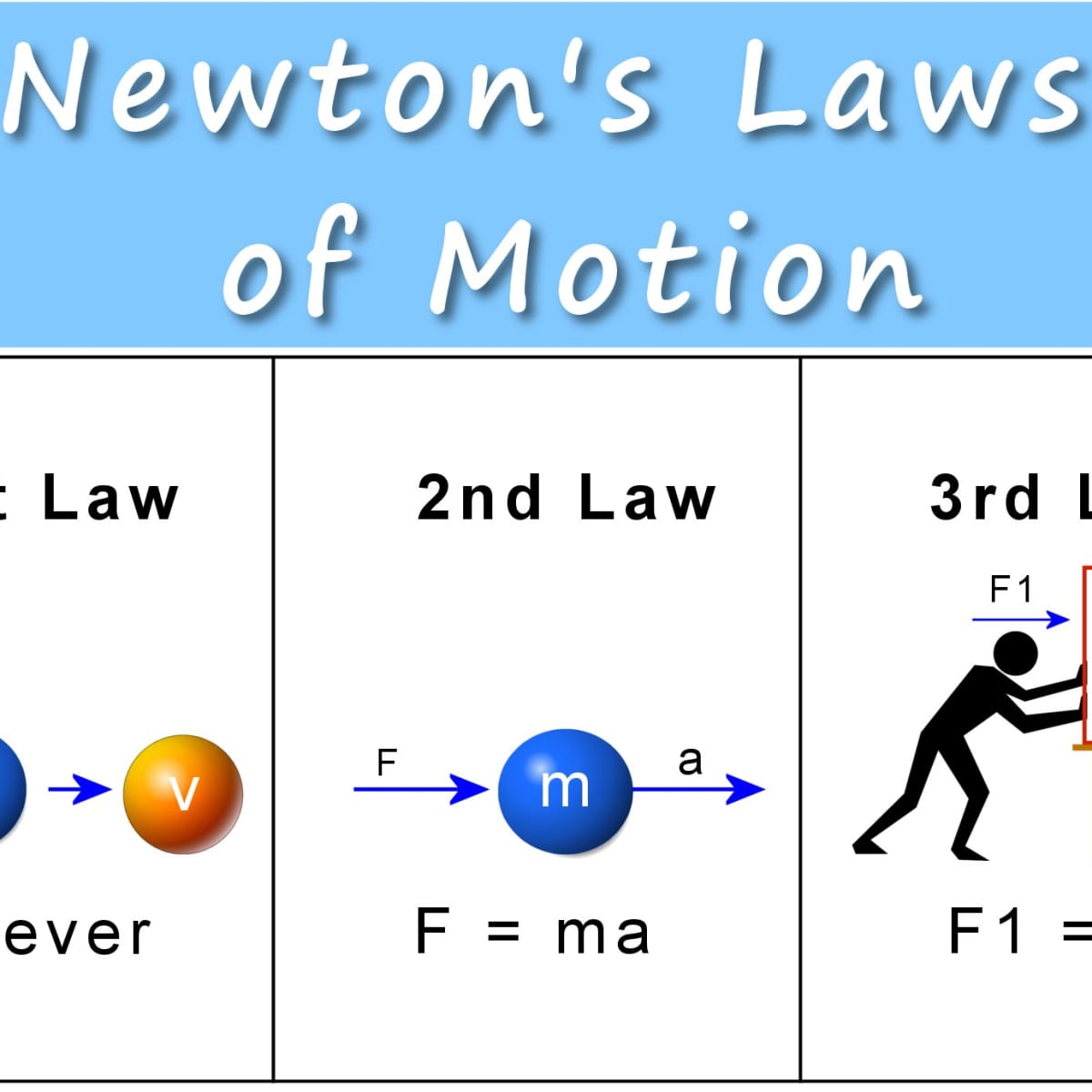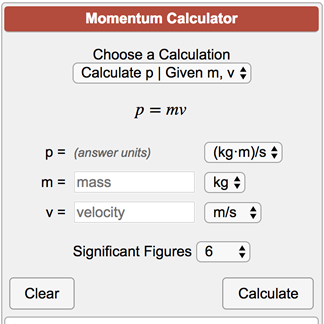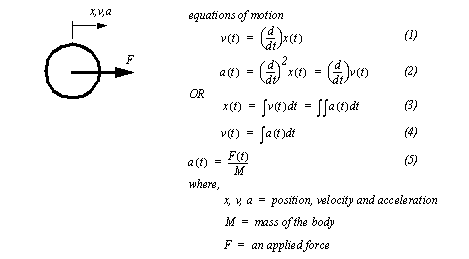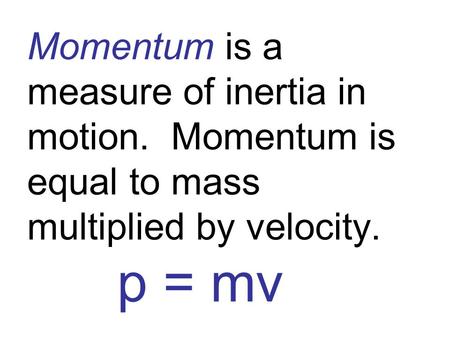
Chapter 7: Momentum I. Momentum (7.1) A. momentum– “inertia in motion” 1. Mass of an object multiplied by its velocity Momentum = mass x velocity. - ppt download

Which takes more force to stop? Big 2m/s Small 2 m/s Big 0.6 m/s Small 6 m/s Small 2 m/s 100 m/s. - ppt download